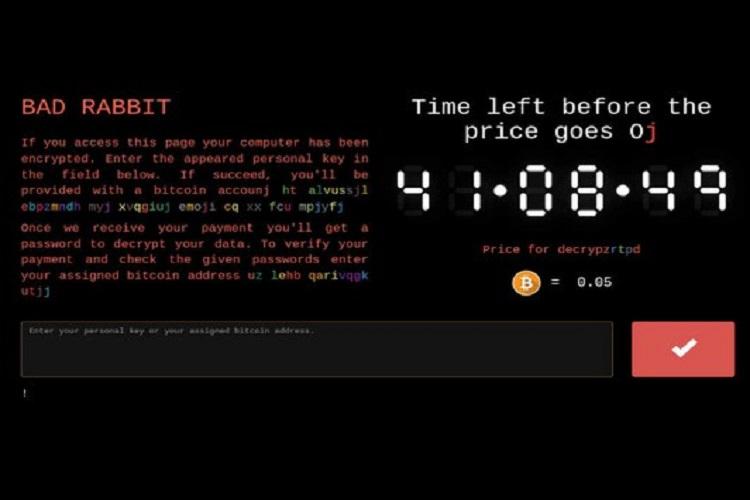
so you have heard! A new kind of malware is spreading around Europe. Dubbed Bad Rabbit, the malware is said to have originated from Russia and Ukraine is now affecting countries such as Turkey and Germany.
Althought the extent of the impact is not yet known, new reports have indicated that the targets include the Ukraine Ministry of Infrastructure and Kiev's public transportation system.
Security vendor Kaspersky has reported that Interfax news agency and Fontanka.ru are among the confirmed victims of the malware. Odessa International Airport has also reported on a cyberattack on its information system. The hackers behind the cyber attack are demanding 0.05 bitcoin as ransom - approximately USD 280, the security vendor has noted.
Kaspersky in its blog also reported that this is a drive-by attack and the victims download a fake Adobe Flash installer from infected websites and manually launch the .exe file, thus infecting themselves. Mostly news or media sites have been impacted by the attack so far.
Another security company Eset, noted in its blog post that there are a number of Russian domains (.ru) that have been affected.

Image courtesy: Avast
Ukraine was been in news for Petya this year in June as a result of poisoned update from MeDoc, which sent out malware disguised as a software update. However, Bad Rabbit is found to be similar in nature to NotPetya.
Kaspersky has also found strong evidence that links Bad Rabbit to the creators of NotPetya. The NotPetya outbreak encrypts the master file table and flashes up a screen requesting a Bitcoin ransom to restore access to the files. It was also known to spread on its own. Possessing similar characteristics, Bad Rabbit could spread like NotPetya. However, so far none of the European, Asian or American countries have reported
To avoid becoming a victim of Bad Rabbit, security companies reccommend:
- Use a strong antimalware/antivirus to block the execution of files c:\windows\infpub.dat and c:\Windows\cscc.dat
- Disable WMI service (if it’s possible in your environment) to prevent the malware from spreading over your network
- Back up your data.
- Don’t pay the ransom

 In
In
Add new comment