
The ongoing impact of COVID-19 pandemic, which has disrupted the traditional business operation landscape, has forced the enterprises to adopt a proactive rather than a reactive approach to address the potential security threats. As a result, security offerings’ revenue in India is estimated to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3% during 2019-2024 to reach USD 4bn in 2024, according to GlobalData.
Rohit Sharma, Senior Technology Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “Key drivers for the security offerings’ revenue growth in India include the increased proliferation of Internet services and mobile broadband penetration, digitalization initiatives across enterprises and evolving security landscape.”
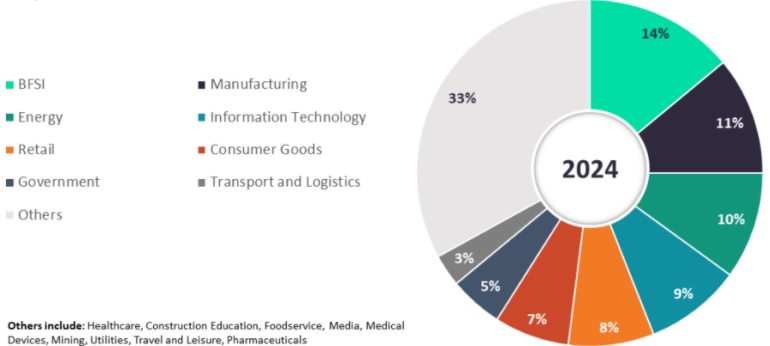
Figure: Security Offerings Revenue by Verticals in India: 2024
Source: GlobalData Market Opportunity Forecasts to 2024: Security
Banking, financial services and insurance (BFSI) vertical will continue to account for the largest share in the security revenue, with increased requirements for security mechanisms like anti-malware and multi-factor authentication.
For instance, in October 2019, State Bank of India (SBI) announced migration of its 30 application systems to CROC’s hybrid cloud for big data management, system fault tolerance improvisation, reliability and security.
Increased digitalization in the manufacturing industry continues to make it prone to cyber threats, as security of the IT assets has traditionally been a secondary priority of these companies. As a result, the companies have started to establish processes/framework to monitor and secure their assets.
For instance, Tata Steel in 2019 announced increase in cybersecurity spending from 8% to 15% within two years and plans to increase it further. JSW Group also continues to re-evaluate its approach towards cyber-security by focusing on information security rather than securing the physical elements containing the information.
The COVID-19 pandemic reshaped the security offerings’ demand for potential cybersecurity solutions, as hackers shifted their attention to tactics like phishing, attacking individual employee accounts with emails and social media posts.
India has formulated a draft for the National Cyber Security Strategy 2020 to create a secure cyberspace. Remote working, sharing of enterprise resources with connected devices and smart cities plans will fuel security spending in India.
Sharma concludes: “The challenges being confronted by enterprises owing to the pandemic and the evolving regulatory landscape will result in the emergence of innovative security offerings and their adoption amongst enterprises.”

 In
In
Add new comment